Phases of Matter and
Thermochemistry Review Sheet
Go to the Answer Key
Chapter 9
- State the kinetic theory of gases.
- What causes gas pressure?
- Convert: a) 456 mm Hg to kPa b) 3.750 atm to kPa c)
-125°C to K
- Explain why evaporation is a cooling process.
- Define allotrope, give 2 examples.
Use the following
phase diagram to answer questions 6-8. Show your answer
on the diagram.
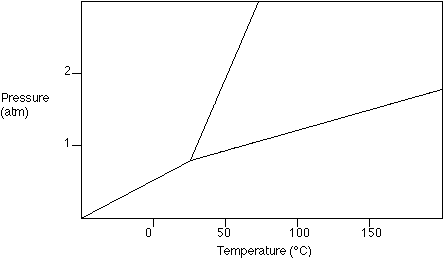
- Label the solid, liquid, and vapor regions.
- What is the boiling point of the substance at 1 atm
pressure?
- What state is a substance in if its temperature is 127°C
at a pressure of 1.5 atm?
- Understand the meaning of figure 9.5 on p.242.
- What are intermolecular forces? How do they play a part
in determining the boiling point of a substance?
- Explain why water boils at a lower temperature here than
at sea level. Include the definition of boiling point.
Chapter 10
You will have to use pp. 266 and 276 for constants for various
problems.
- How much heat, in joules, is required to raise the
temperature of 45.0 mL of water from 14.0 °C to 48.0
°C?
- a) How much energy, in calories and in joules, is
required to warm 197.25 g of grain alcohol (ethanol) from
22.0 °C to 37.0 °C?
b) Would the same amount of water require less, more, or
the same amount of heat? Explain.
- How much heat is required to boil 76 grams of water?
- A 120.0 gram piece of ice is removed from a refrigerator
at -11.0 °C, placed in a glass, allowed to melt, and
finally warmed up to room temperature, 21.0 °C. How much
heat has the final water absorbed from the atmosphere?
- How much heat will be released in burning 78.4 g of C2H4?
DH = -1390 kJ for the
combustion reaction.
- Calculate DHrxn for
each of the following reactions, using the H°f
found in appendix A, table A.6 in the book.
a) 2 NO(g) + O2(g) --> 2 NO2(g)
b) Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g)
--> 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g)
- Given: MnO2(s) --> MnO(s) + 1/2
O2(g) DH = +32.5
kcal
MnO2(s) + Mn(s) --> 2 MnO(s)
DH = -59.5 kcal
Find Hf of MnO2 (the heat of
formation of MnO2 from its elements).
- Find DH for the following
reaction using the information given below.
2 Na2O2(s) + 4 HCl(g)
--> 4 NaCl(s) + 2 H2O(1)
+ O2(g)2 Na2O2(s) + 2
H2O(l) --> 4 NaOH(s)
+ O2(g) DH = -30.2
kcal
NaOH(s) + HCl(g) --> NaCl(s)
+ H2O(l) DH
= -42.8 kcal
- How much heat, in kJ, is needed to boil away 100.0 g
grain alcohol (ethanol) at 25.0°C.
- A 1.50 g piece of gold absorbed 0.162 cal when its
temperature was raised by 3.50 °C. Calculate the
specific heat of gold in cal/(g °C) and J/(g °C).
Answers: 12) 6,400 J 13) 1700 cal, 7100 J 14) 170 kJ 15) 53.3 kJ 16) 3880 kJ
17) a) -113.04 kJ 17b) -26.9 kJ 18) -124.5 kcal 19) -201.4 kcal 20) 107 kJ
21) 0.0309 cal/(g °C), 0.129 J/(g °C)
Return to Chemistry 30

